- Scientific Name
- Farancia abacura abacura
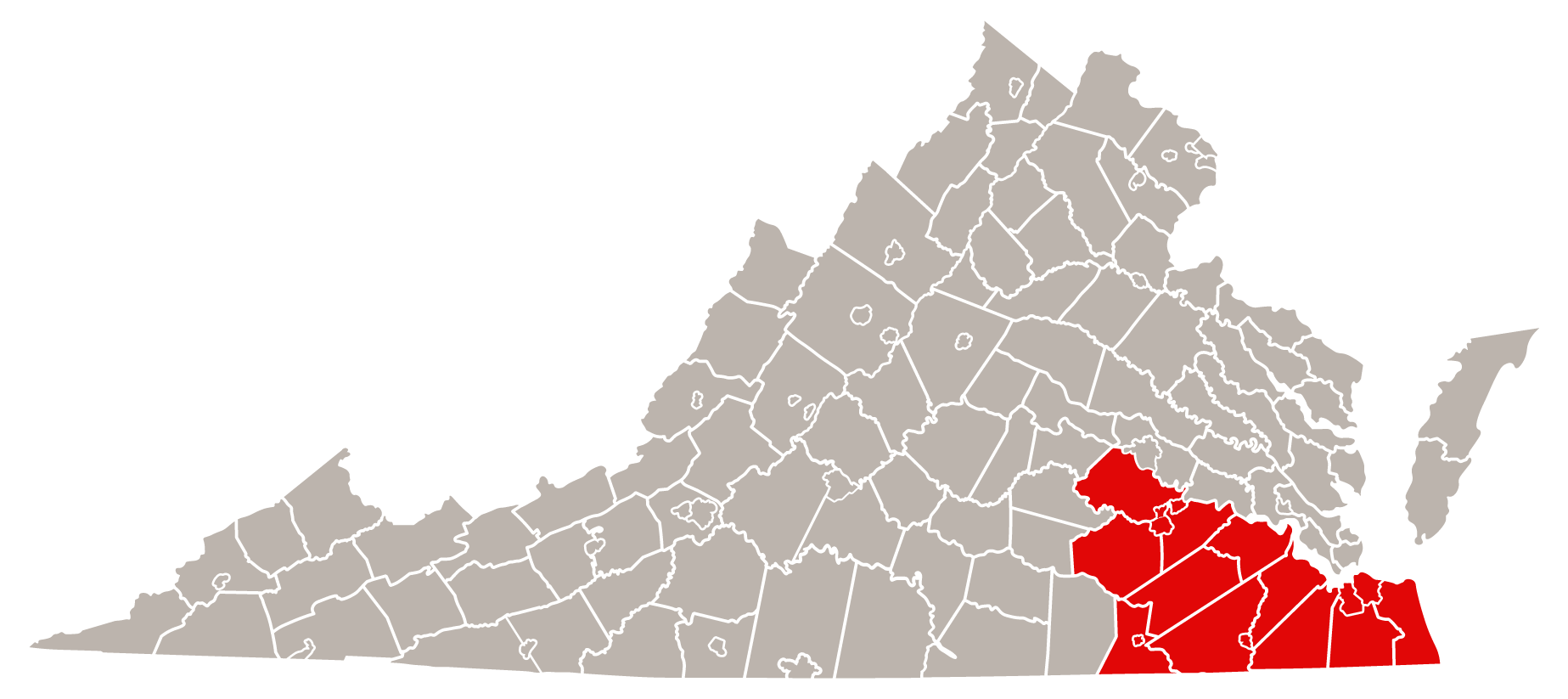
- Range
- Southeast Virginia
- Also Known As
- Hoop Snake, Stinging Snake
- Venomous
- No
- Features
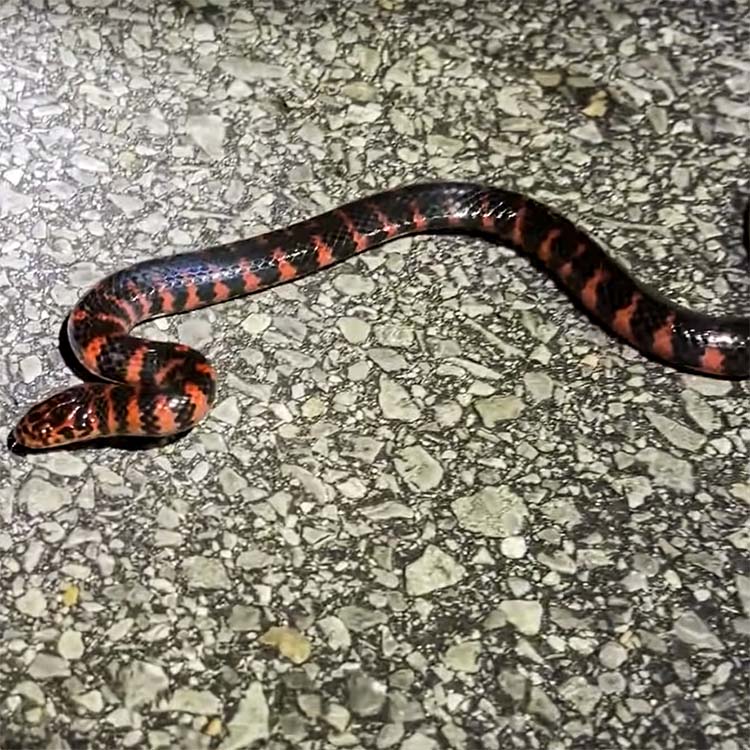
- Black Body With a Red Belly
- Prey
- Salamanders and Amphibians
- Litter Size
- 6 - 104 Eggs per Birth
- Life Span
- 19 Years (in Captivity)
- Length
- 40 - 54 Inches
Quick Links for Eastern Mud Snake
Eastern Mud Snake Description
Eastern Mud Snake Appearance
The main body of the snake is a shiny black with red or pink belly. The belly coloration extends in blotches in triangular shape upwards giving appearance of alternating red and black blotches.
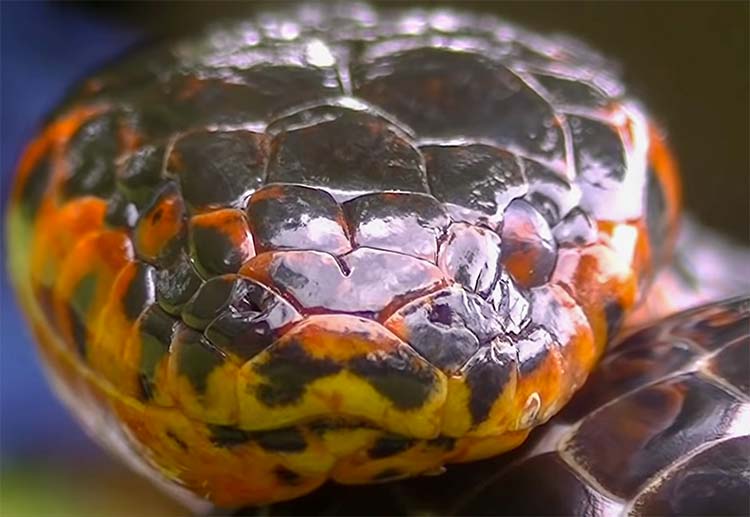
The chin and throat will be a yellow color.
Size
This snake is usually between 40 to 54 inches long.
The record length found was about 85.1 inches long. (Virginia’s record length is about 58.6).
Juveniles tend to be 7 to 10.25 inches long.
Eastern Mud Snake Behavior
These snakes are aquatic and they rarely leave the water, except for egg laying, hibernation during the winter, and to move to other bodies of water.
These snakes do not bite even when being held. Despite being called “the stinging snake” these snake do not sting but uses their tail to prod prey.
There is the myth that these snakes will bite their tail and “roll” after people and prey. Giving them the name Hoop Snake. This is not true, and this phenomenon has not been observed for these snakes
Range and Habitat
Range
These snakes can be found found in southeastern Virginia, but can sometimes be found outside their range. These snakes’ range extends all the way down to Florida, and southeast Virginia is their most northern range.
Habitat
These snakes prefer slow-moving streams, canals, swamps, and forested wetlands. In other words, where there is shallow water, there are these snakes.
Diet of Eastern Mud Snake
These snakes are carnivores. They prey mostly on giant aquatic salamanders, but also eat other amphibians. These snakes can also hunt for fish in the water.
Reproduction and Young
Reproduction
These snakes’ breeding season starts in July and ends in September. During the mating season, females release pheromones from their skin to attract males. To humans these pheromones smell horrible and can stain.
Eggs and Young
Eggs are laid in July or early September and hatch 56 days later.